Cougar
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Felidae
Genus: Puma
Scientific Name: Puma concolor
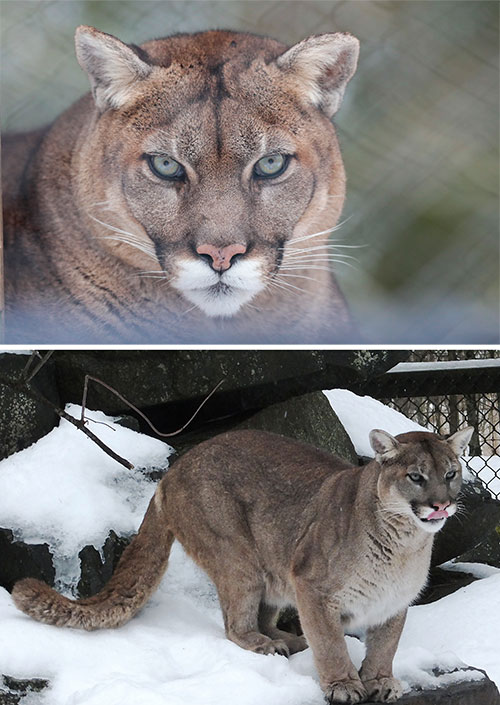
Description: Weighing between 40-85 kg (88-188 lbs), the cougar is by far the largest wild cat found in North America. Cougars tend to be one solid colour in shades ranging from tan to very dark brown or black. Although adult male cougars can reach lengths of 2.7m (9ft), their long tail accounts for nearly half their total length.
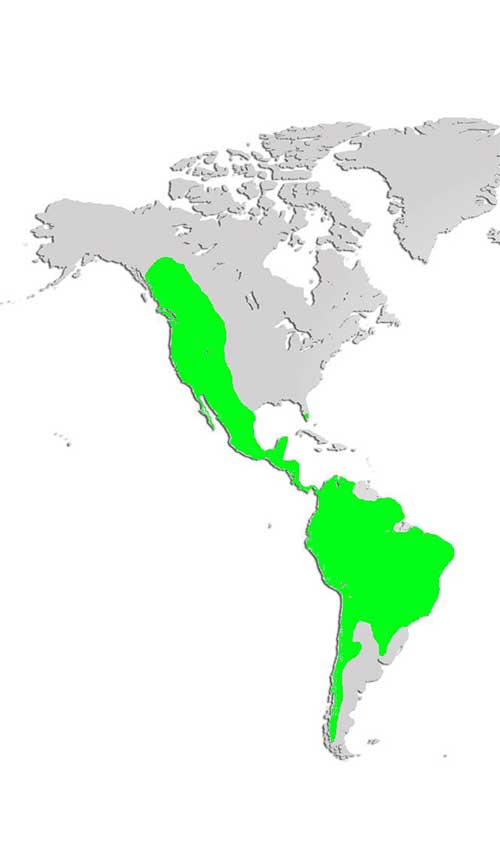
Distribution and Habitat: Also known as mountain lions, or pumas, cougars are found in western Canada and south through the USA to the tip of South America. Solitary animals, cougars prefer wooded and mountainous areas, but have been known to swim across rivers and out to islands to hunt.
Diet: Carnivores, cougars prefer large ruminants like moose, deer and mountain sheep, but they will hunt smaller animals as well.
Life Cycle: Although cougars are able to breed year round, they tend to mate in late winter. One male will mate will multiple females and competition for females is intense. Following a 90 day gestation, 3-6 kittens are born in a litter (rarely more than 3 survive) with their eyes closed. Kittens remain with their mother for 18 to 24 months and after that live a mostly solitary existence.
Adaptations: The cougar’s long tail gives it excellent balance when both running and climbing. When competing with wolves or other terrestrial predators for food, cougars will climb into trees and pursue their prey from above.
Did you know? Cougars have jaws so strong they can snap a spinal cord or windpipe with one bite. They are so prevalent in North America that they hold the record for the land mammal with the most names.